


In June 2024, AI organization Databricks made three major announcements, capturing attention in the data science and engineering sectors. The company introduced advancements set to streamline user experience, improve data management, and facilitate data engineering workflows.
The first significant development is the new generation of Databricks Notebooks. With its focus on data-focused authoring, the Notebook…

Topological Deep Learning (TDL) has advanced beyond traditional Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) by modeling complex multi-way relationships, which is imperative for understanding complex systems like social networks and protein interactions. A key subset of TDL, known as Topological Neural Networks (TNNs), are proficient at handling higher-order relational data and have demonstrated superior performance in various…
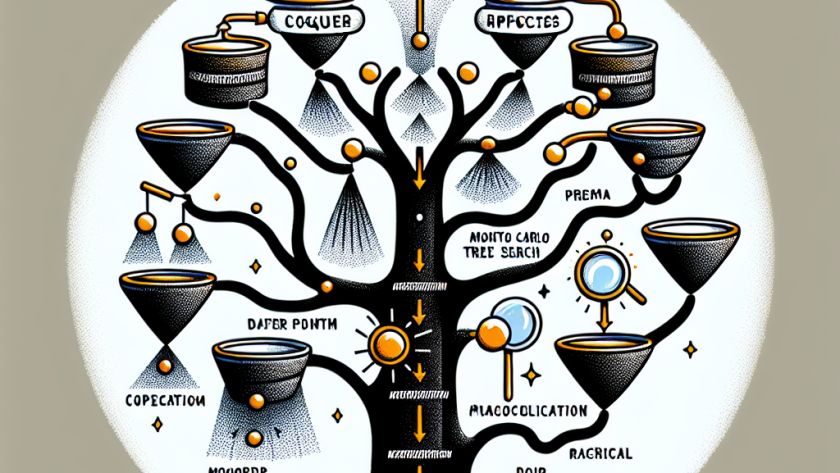
Artificial intelligence (AI) with large language models (LLMs) have made major strides in several sophisticated applications, yet struggle with tasks that require complex, multi-step reasoning such as solving mathematical problems. Improving their reasoning abilities is vital for improving their efficiency on such tasks. LLMs often fail when dealing with tasks requiring logical steps and intermediate-step…

Robotic manipulation policies are currently limited by their inability to extrapolate beyond their training data. While these policies can adapt to new situations, such as different object positions or lighting, they struggle with unfamiliar objects or tasks, and require assistance to process unseen instructions.
Promisingly, vision and language foundation models, like CLIP, SigLIP, and Llama…

The evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) requires a systematic and multi-layered approach to accurately identify areas of improvement and limitations. As these models advance and become more intricate, their assessment presents greater challenges due to the diversity of tasks they are required to execute. Current benchmarks often employ non-precise, simplistic criteria such as "helpfulness"…

Machine unlearning refers to the efficient elimination of specific training data's influence on a trained AI model. It addresses legal, privacy, and safety issues arising from large, data-dependent AI models. The primary challenge is to eliminate specific data without the expensive and time-consuming approach of retraining the model from scratch, especially for complex deep neural…

The Allen Institute for AI has recently launched the Tulu 2.5 suite, a revolutionary progression in model training employing Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). The suite encompasses an array of models that have been trained on several datasets to augment their reward and value models, with the goal of significantly enhancing…

DeepMind researchers have presented TransNAR, a new hybrid architecture which pairs the language comprehension capabilities of Transformers with the robust algorithmic abilities of pre-trained graph neural networks (GNNs), known as neural algorithmic reasoners (NARs. This combination is designed to enhance the reasoning capabilities of language models, while maintaining generalization capacities.
The routine issue faced by…

Machine learning is a crucial domain where differential privacy (DP) and selective classification (SC) play pivotal roles in safeguarding sensitive data. DP adds random noise to protect individual privacy while retaining the overall utility of the data, while SC chooses to refrain from making predictions in cases of uncertainty to enhance model reliability. These components…

Large Language Models (LLMs) present a potential problem in their inability to accurately represent uncertainty about the reliability of their output. This uncertainty can have serious consequences in areas such as healthcare, where stakeholder confidence in the system's predictions is critical. Variations in freeform language generation can further complicate the issue, as these cannot be…
